Optical fiber undoubtedly plays a key role in modern communication networks. This article will compare the main features of single-mode OFC and multi-mode OFC. We will first define the physical structure and optical properties of single-mode OFC and explain its advantages in high-speed transmission. Next, we will describe the physical structure and optical mechanism of the multimode OFC and illustrate its applicability in certain applications.
Subsequently, we will compare the differences between the two in parameters such as fiber core diameter and numerical aperture, and analyze their differences in optical signal propagation characteristics, transmission distance, etc. In addition, we will list the typical applications of single-mode OFC and multi-mode OFC in networks, data centers and other fields, and analyze the factors to consider when selecting based on actual needs. Finally, we will introduce the technical requirements and precautions for both maintenance and management.

What is single-mode OFC
Let me introduce to you the basic concepts of Single-Mode Optical Fiber Communication (Single-Mode Optical Fiber Communication, referred to as single-mode OFC):
Physical structure and optical properties of single-mode OFC:
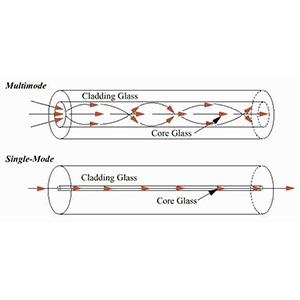
- Single-mode fiber has a very small core diameter (8-10 microns) and can only transmit a single light wave mode.
- The core of the optical fiber is made of high refractive index material, and the cladding is made of low refractive index material.
- Single-mode fiber only allows one basic mode (LP01 mode) to propagate within the fiber, and no higher-order modes.
- Single-mode fiber has better dispersion and loss characteristics than multi-mode fiber and is suitable for long-distance transmission.
Advantages of single-mode OFC in high-speed transmission:
1. High bandwidth potential:
- Single-mode optical fiber can transmit higher optical signal bandwidth and support high-speed transmission at the Gbps level.
- Through WDM technology, multiple wavelengths can be transmitted in parallel on one optical fiber, greatly increasing bandwidth.
2. Low transmission loss:
- The inherent loss coefficient of single-mode fiber is low, usually around 0.2dB/km.
- This enables single-mode OFC to transmit without relays within tens of kilometers, significantly reducing the need for relays.
3. Strong anti-interference:
- Single-mode optical fiber has a small diameter and has strong anti-interference ability against electromagnetic interference and environmental factors.
- This ensures the reliability and stability of signal transmission and is suitable for applications in harsh environments.
4. Low dispersion characteristics:
- Single-mode fiber has a low dispersion coefficient, which can effectively suppress the impact of dispersion on high-speed signals.
- No need for complex dispersion compensation measures, simplifying system design.
In summary, single-mode OFC has played a key role in high-speed and long-distance optical communications with its excellent physical and optical properties, and has become the mainstream technology of modern optical fiber communications.
What is multi-mode OFC
Let me introduce to you the basic concepts of multimode optical fiber communication (Multimode Optical Fiber Communication, referred to as multimode OFC):
Physical structure and optical mechanism of multimode OFC:
- Multimode fiber has a larger core diameter (50-100 microns) and can accommodate multiple propagation modes.
- The refractive index difference between the fiber core and the cladding is large, which is conducive to the propagation of multiple higher-order modes in the fiber.
- Due to the inter-modal dispersion effect, propagation delay differences will occur between different modes.
- This inter-modal dispersion will cause signal distortion at the receiving end, limiting transmission bandwidth and distance.
Applicability of multimode OFC in certain applications:
1. Short distance transmission:
- Inter-mode dispersion has less impact on short-distance transmission, and multi-mode OFC can provide a lower-cost solution.
- Widely used in scenarios such as local area networks such as LANs and buildings, as well as internal access in data centers.
2. Low rate transmission:
- In low-speed transmission, inter-modal dispersion has less impact on signal quality.
- Suitable for some traditional video surveillance, sensor network and other applications that do not have high bandwidth requirements.
3. Optical fiber access scenario:
- Multimode optical fiber has lower cost and is suitable for the last mile access network.
- Some FTTH (Fiber to the Home) solutions will use multi-mode OFC as the access segment.
4. Simplify system design:
- Multi-mode optical fiber is more flexible and convenient in terms of optical signal coupling and optical connection.
- It can simplify the structure and debugging requirements of optical transceiver equipment.
In general, although multi-mode OFC has relatively low bandwidth and transmission distance, it still has a place in certain application scenarios due to its cost advantage and system simplicity. With the continuous advancement of technology, multi-mode OFC will continue to play an important role in low-cost short-distance communications in the future.
What are the differences between single-mode OFC and multi-mode OFC
Let me compare the main technical parameters and performance differences between single-mode optical fiber communication (single-mode OFC) and multi-mode optical fiber communication (multi-mode OFC):
Fiber core diameter and numerical aperture:
- Single-mode optical fiber has a small core diameter (8-10 microns) and only supports the propagation of a single basic mode.
- Multimode fiber has a larger core diameter (50-100 microns) and can accommodate multiple high-order propagation modes.
- The numerical aperture (NA) of single-mode fiber is small (usually around 0.1), and the NA of multi-mode fiber is large (above 0.2).
Optical signal propagation characteristics:
- Single-mode optical fiber has only one basic mode of propagation and does not produce inter-modal dispersion.
- Multi-mode optical fiber has multiple propagation modes, which will produce inter-mode dispersion and limit the transmission bandwidth.
- Single-mode fiber has better dispersion characteristics and signal-to-noise ratio, and is suitable for high-speed transmission.
Transmission distance and bandwidth:
- Single-mode optical fiber can transmit long distances of tens to hundreds of kilometers, and the bandwidth can reach Gbps level.
- The transmission distance of multi-mode optical fiber is generally within 2-3 kilometers, and the bandwidth is lower than that of single-mode.
System design and cost:
- Single-mode optical fiber systems have higher requirements for light sources, photodetectors, optical couplings, etc., and are more expensive.
- The light source and optical coupling of the multimode optical fiber system are relatively simple and low in cost.
- Multimode optical fiber is more suitable as an economical choice for the last mile access network.
In general, single-mode OFC and multi-mode OFC have their own advantages and are suitable for different application scenarios. Single-mode OFC is more suitable for high-speed and long-distance transmission, while multi-mode OFC is more suitable for low-cost, short-distance LAN and access network applications. In actual deployment, appropriate optical fiber communication solutions need to be selected based on specific network requirements.
Selection comparison of application scenarios
Let me compare for you the use of single-mode optical fiber communication (single-mode OFC) and multi-mode optical fiber communication (multi-mode OFC) in different application scenarios:
Network application scenarios:
- Backbone network/Metropolitan area network: Single-mode OFC is suitable and can provide high bandwidth and long-distance transmission.
- Enterprise campus network/building network: Multi-mode OFC is suitable, low cost, and suitable for short-distance transmission.
- Wireless access aggregation: suitable for single-mode OFC, carrying large-capacity wireless traffic aggregation.
Data center application scenarios:
- Internal interconnection in the computer room: Single-mode OFC is suitable and can provide ultra-high bandwidth at the Tbps level.
- Computer room to computer room interconnection: Single-mode OFC is suitable for high-speed and long-distance interconnection.
- Access network/terminal access: Multi-mode OFC is applicable and the cost advantage is obvious.
Consideration factors when choosing single-mode or multi-mode OFC:
1. Transmission distance and bandwidth requirements:
- For long-distance, high-bandwidth applications, single-mode OFC is more suitable.
- For short-distance, low-bandwidth applications, multi-mode OFC can provide an economical solution.
2. System cost and complexity:
- Single-mode OFC has higher technical requirements for light source, optical transceiver, optical coupling, etc. and higher cost.
- The system design and debugging of multi-mode OFC is relatively simple and low cost.
3. Environmental factors and reliability:
- Single-mode OFC has stronger anti-interference and reliability, and is suitable for harsh environments.
- Multi-mode OFC is highly sensitive to environmental factors and is suitable for relatively good environments.
To sum up, in practical applications, single-mode OFC or multi-mode OFC need to be weighed based on transmission distance, bandwidth, cost, reliability and other factors. These two optical fiber communication technologies have their own advantages and are suitable for different network scenarios and application requirements.
Differences between installation, debugging and maintenance management
Let me compare the differences between single-mode optical fiber communication (single-mode OFC) and multi-mode optical fiber communication (multi-mode OFC) in terms of installation, commissioning and daily maintenance and management:
Technical requirements for connection and welding:
1.Single-mode OFC:
- High requirements for optical fiber end face cleanliness and alignment accuracy require professional tools and training.
- The quality of welding directly affects the transmission performance, requiring the use of high-precision welding equipment.
- Connector alignment and docking accuracy are key, and high-precision equipment such as heat shrink joints are often used.
2.Multi-mode OFC:
- The requirements for optical fiber end face cleanliness and alignment accuracy are relatively loose.
- Welding quality has little impact on transmission performance, and ordinary welding equipment can be used.
- Connector alignment and docking are relatively simple, and simple mechanical docking methods can be used.
Daily maintenance and fault diagnosis:
1.Single-mode OFC:
- It is necessary to regularly check the cleanliness of the fiber end face to prevent the increase in loss caused by contamination.
- Use professional testing tools such as OTDR to diagnose fiber link losses and fault points.
- The requirements for troubleshooting and positioning are relatively strict and require professional maintenance personnel.
2.Multi-mode OFC:
- Fiber end face maintenance requirements are relatively loose, and regular simple cleaning is sufficient.
- Basic test tools such as power meters can be used to diagnose link performance and locate faults.
- Troubleshooting is relatively simple and can be completed by general maintenance personnel.
In general, single-mode OFC has high technical requirements in connection, welding, maintenance, etc., and requires professional tools and personnel. Multi-mode OFC is relatively simple and flexible in these aspects, and is easier to master by ordinary network maintenance personnel. Therefore, when selecting OFC technology, the capability level of the existing operation and maintenance team must also be considered.
Summary
Single-mode OFC and multi-mode OFC are the core components of optical fiber communication systems, and their selection and management are crucial to the performance and reliability of the entire network. Our company has long been focused on the research and development and application of optical fiber communication technology and has rich industry experience. Our single-mode OFC and multi-mode OFC products have reached industry-leading levels in terms of optical parameters, transmission performance, etc., and can meet your demanding communication needs.
Whether you need to deploy it on a backbone network or an access network, we can provide you with customized OFC solutions. At the same time, our professional team will provide you with a full range of technical support, including on-site installation guidance, daily maintenance training, etc. Contact us now to learn more details about single-mode OFC and multi-mode OFC.
Single-mode OFC and multi-mode OFC FAQ
Single-mode optical fiber has a very small core diameter (typically 8-10 microns) that allows only a single mode of light to propagate through the fiber.
Multimode optical fiber has a larger core diameter (typically 50-100 microns) that can support the propagation of multiple modes of light.
The core size is the main difference, which leads to differences in performance characteristics, such as attenuation, bandwidth, and transmission distance.
Single-mode OFC have lower attenuation, higher bandwidth, and can support longer transmission distances compared to multimode OFC, making them more suitable for long-haul and high-speed communications.
Multimode OFC are generally less expensive, easier to work with, and can be used for shorter-distance applications, such as within buildings or campus networks.
Single-mode OFC typically operate at 1310 nm and 1550 nm, while multimode OFC commonly use 850 nm and 1300 nm wavelengths.
Single-mode OFC require more precise termination and splicing techniques due to their smaller core size, while multimode OFC are generally easier to work with.
Single-mode OFC are widely used in long-distance telecommunications, fiber-to-the-home (FTTH), and high-speed data center networks, while multimode OFC are commonly found in shorter-distance local area network (LAN) and industrial applications.
Single-mode OFC have lower dispersion and can support higher data rates over longer distances, while multimode OFC are more susceptible to modal dispersion, limiting their bandwidth and transmission range.
Ongoing advancements include the development of higher-capacity single-mode fibers, such as those supporting wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM), and the introduction of new multimode fiber types to support higher data rates in shorter-reach applications.